electron affinity simple definition|electron affinity trend and exceptions : Cebu Ionization potential is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Energy is supplied for removing an electron implies that energy will be released if . Tingnan ang higit pa Summary. The main focus with this release is bringing our support up to date for both the GCC and Arm compilers, so GCC10 and Arm 6.15.0 respectively, and .
PH0 · trend for electron affinity
PH1 · electron affinity vs electronegativity
PH2 · electron affinity trend and exceptions
PH3 · electron affinity equation
PH4 · electron affinity chart
PH5 · Iba pa
GTA mods and Gaming Optimization tweaks! Find everything hereAll problem solution you will find here realted to PC optimization for gaming.Business Email: ga.
electron affinity simple definition*******The amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form an anion is called electron affinity. Electron affinities are difficult to measure. 1. Electron affinity increases going left to right across a period because of increased nuclear attraction. 2. Going down the group the . Tingnan ang higit paElectron affinity is defined as The electron affinity is the potential energy change of the atom when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atomto form a negative ion. So the more negative the electron affinity the . Tingnan ang higit pa
Ionization potential is the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. Energy is supplied for removing an electron implies that energy will be released if . Tingnan ang higit paThe general factors that affect electron affinity are listed below. 1. \(\begin{array}{l}Electron\ affinity = \frac{1}{Atomic\ Size}\end{array} \) 2. \(\begin{array}{l}Electron\ affinity = Effective\ . Tingnan ang higit pa
electron affinity trend and exceptionsThe electron affinity (Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion. X(g) + e → X (g) + energyThis differs by sign from the energy change of electron capture ionization. The electron affinity is positive when energy is released on electron capture. Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a . Electron affinity is a measure of how readily a neutral atom gains an electron. Electron affinity ( E ea ) is the energy change when an electron is added to a .
electron affinity simple definitionThe energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to produce a negatively charged ion is called electron affinity. Only a few chemical elements, mostly halogens, have measured electron affinities. Electron affinity is defined as the quantitative measurement of the energy change that results from adding a new electron to a neutral atom or molecule in the .Definition: Electron Affinity defined as removal of an electron. Electron affinity can be defined as the energy required when an electron is removed from a gaseous anion. .
electron affinity simple definition electron affinity trend and exceptionsElectron affinity is the energy change that results from adding an electron to a gaseous atom. For example, when a fluorine atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form .
Electron affinity is the amount of energy required to detach one electron from a negatively charged ion of an atom or molecule. It is indicated using the symbol Ea and is usually expressed in units of .The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy .Chemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This process creates a negative ion. This process differs from .The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (7.5.1) (7.5.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is .Electron affinity can be defined as the energy required when an electron is removed from a gaseous anion. The reaction as shown in equation 2.3.2.1 2.3.2.1 is endothermic (positive ΔU Δ U) for elements except noble gases and alkaline earth metals. Under this definition, the more positive the EA value, the higher an atom's affinity for electrons. Electron affinity can be defined as the energy required when an electron is removed from a gaseous anion. The reaction as shown in equation 2.3.2.1 2.3.2.1 is endothermic (positive ΔU Δ U) for elements except noble gases and alkaline earth metals. Under this definition, the more positive the EA value, the higher an atom's affinity for .The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy change=EA (8.5.1) (8.5.1) E ( g) + e − → E ( g) − energy change= E A. Unlike ionization energies, which are always positive for a neutral atom because energy is required . Definition of Electron Affinity. Electron affinity is a quantitative measurement of the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher the electron affinity and the more easily an electron is added to an atom. Electron affinity can be .
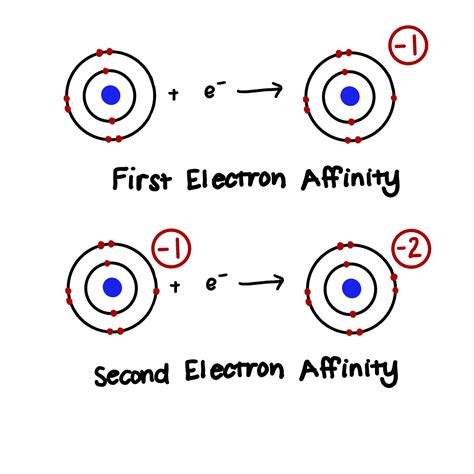
The electron affinity ( EA) is the energy released to add an electron to an elements in the gaseous state. In general successive electron affinity increase in magnitude EA1 < EA2 < EA3 and so on. First electron affinity increases across the period. First electron affinity decreases down the group.
The electron affinity of an element is defined as the energy released when an electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom to form a gaseous anion, or negative ion. Usually, only one electron is added, forming a uninegative ion. Since energy is evolved, these terms have a negative sign. Generally, electron affinities become more negative across a row of the periodic table. Figure 1.1.2.4.2 Electron Affinities (in kJ/mol) of the s -, p -, and d -Block Elements. In general, electron affinities of the main-group elements become less negative as we proceed down a column. This is because as n increases, the extra electrons enter .
Electron affinity is the energy produced when a gaseous neutral atom absorbs an electron and becomes a negatively charged ion. When the initial electron is added to an atom, a monovalent anion is released, releasing energy. Adding another electron to this anion repels it, absorbing energy. Further electron affinities are positive.
The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity .The first electron affinity is the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous atoms each acquire an electron to form 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions. This is more easily seen in symbol terms. X (g) + e - X - (g) It is the energy released (per mole of X) when this change happens. First electron affinities have negative values.
Electron affinity is defined as the quantitative measurement of the energy change that results from adding a new electron to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher an atom’s affinity for electrons.The energy of an atom is stated when an atom loses or gains energy . Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures!In this video I will give the definition of the electron affinity.Electron affinity. Third in importance for bond formation after size and ionization energy is the energy change accompanying the attachment of electrons to a neutral atom. This energy is expressed as the electron affinity, which is the energy released when an electron is attached to an atom of the element. In many cases, the electron affinity .Electron affinity is the energy change that results from adding an electron to a gaseous atom. For example, when a fluorine atom in the gaseous state gains an electron to form F⁻ (g), the associated energy change is -328 kJ/mol. Because this value is negative (energy is released), we say that the electron affinity of fluorine is favorable.
Definition: Electron Affinity of an Atom. The electron affinity of an atom is the energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gas state to form a negative ion, per mole of atoms. Electron affinities are usually expressed in kilojoules per mole ( kJ/mol ). We also use the word electron affinity to refer to the overall .
One of the most dreaded questions in the quantitative aptitude exams of all banking and competitive exams is the odd man out series questions. This is because to answer such questions students must follow only reasoning powers and logic, there are no formulas or equations to help you out. However, you can keep a few pointers in mind.
electron affinity simple definition|electron affinity trend and exceptions